AnnotateRbを読んで、処理の流れを図解してみた
AnnotateRbというgemのソースコードを読んだのでアウトプットを兼ねてまとめをしてみました。
また今回は Model ファイルに注釈を追加する処理に絞ってコードを読んでみました。
理由としては、このgemで追加されるRakeタスクはModelファイルへの注釈にのみ対応しているためです。
このあたりで説明がなされています。
Annotate gem added 4 rake commands: annotate_models, remove_annotation, annotate_routes, remove_routes that were removed. If you use these and would like them back please open an issue. https://github.com/drwl/annotaterb/blob/main/MIGRATION_GUIDE.md
目次
bundle install からAnnotateRbが実行されるまで
bundle installを実行した後に以下コマンドを実行します。
bin/rails g annotate_rb:install
このコマンドではgenerators配下のinstall_generatorが呼ばれます。
# lib/generators/annotate_rb/install/install_generator.rb
# frozen_string_literal: true
require "annotate_rb"
module AnnotateRb
module Generators
class InstallGenerator < ::Rails::Generators::Base
def install_hook_and_generate_defaults
generate "annotate_rb:hook"
generate "annotate_rb:config"
end
end
end
end
ここでは以下の役割を持つgeneratorが呼ばれています。
rails db:migrate等の処理にhookして、AnnotateRbを実行させる設定を持ったRakeタスクを追加- 設定ファイルをProjectに追加
上述のgenerate "annotate_rb:hook"では以下の処理が行われます。
# frozen_string_literal: true
require "annotate_rb"
module AnnotateRb
module Generators
class HookGenerator < ::Rails::Generators::Base
source_root File.expand_path("templates", __dir__)
def copy_hook_file
copy_file "annotate_rb.rake", "lib/tasks/annotate_rb.rake"
end
end
end
end
ここではProjectにファイルがコピーされるだけなので、実行まではされません..
追加されたRakeタスクはいつ実行される?
自分はこの点がわからずでしたのもう少し追ってみました。
rails db:migrate等の処理にhookして、AnnotateRbを実行させる設定を持ったRakeタスクを追加
初めに以下のRakeタスクがProjectに追加されます。
## lib/annotate_rb/tasks/annotate_models_migrate.rake
# These tasks are added to the project if you install annotate as a Rails plugin.
# (They are not used to build annotate itself.)
# Append annotations to Rake tasks for ActiveRecord, so annotate automatically gets
# run after doing db:migrate.
# Migration tasks are tasks that we'll "hook" into
migration_tasks = %w[db:migrate db:migrate:up db:migrate:down db:migrate:reset db:migrate:redo db:rollback]
# Support for data_migrate gem (https://github.com/ilyakatz/data-migrate)
migration_tasks_with_data = migration_tasks.map { |task| "#{task}:with_data" }
migration_tasks += migration_tasks_with_data
if defined?(Rails::Application) && Rails.version.split(".").first.to_i >= 6
require "active_record"
databases = ActiveRecord::Tasks::DatabaseTasks.setup_initial_database_yaml
# If there's multiple databases, this appends database specific rake tasks to `migration_tasks`
ActiveRecord::Tasks::DatabaseTasks.for_each(databases) do |database_name|
migration_tasks.concat(%w[db:migrate db:migrate:up db:migrate:down].map { |task| "#{task}:#{database_name}" })
end
end
migration_tasks.each do |task|
next unless Rake::Task.task_defined?(task)
Rake::Task[task].enhance do # This block is ran after `task` completes
task_name = Rake.application.top_level_tasks.last # The name of the task that was run, e.g. "db:migrate"
Rake::Task[task_name].enhance do
::AnnotateRb::Runner.run(["models"])
end
end
end
これは、スクリプト形式であるためrails db:migrateのようなRakeタスクが呼び出された場合に、Rakefile内の処理によりロード & 実行されるため、設定が反映されます。
# Rakefile
# Add your own tasks in files placed in lib/tasks ending in .rake,
# for example lib/tasks/capistrano.rake, and they will automatically be available to Rake.
require_relative "config/application"
Rails.application.load_tasks
設定ファイルload ~ 注釈実行クラス呼び出し
上記のRakeタスクが実行された後は、rails db:migrate等の実行後に以下のコマンドが実行されるようになります。
::AnnotateRb::Runner.run(["models"])
上記コマンドが実行されると以下の箇所が呼び出されます。
# lib/annotate_rb/runner.rb
# frozen_string_literal: true
module AnnotateRb
class Runner
class << self
def run(args)
new.run(args)
end
end
def run(args)
config_file_options = ConfigLoader.load_config
parser = Parser.new(args, {})
parsed_options = parser.parse
remaining_args = parser.remaining_args
options = config_file_options.merge(parsed_options)
@options = Options.from(options, {working_args: remaining_args})
AnnotateRb::RakeBootstrapper.call(@options)
if @options[:command]
@options[:command].call(@options)
else
# TODO
raise "Didn't specify a command"
end
end
end
end
ここでは主に以下のことを行なっています。
- YAML形式の設定ファイルをloadし、Rubyオブジェクトに変換
- 変換したオブジェクトと引数をまとめて、インスタンス変数に格納
- 指定されたコマンドを実行
@optionsには以下のような値が格納されています。
#<AnnotateRb::Options:0x000000010afb5148
@options=
{:position=>"before",
.
.
# 省略
.
:command=>#<AnnotateRb::Commands::AnnotateModels:0x000000010afb62a0>,
:original_args=>["models"]},
@state={:working_args=>[]}>
そのため、以下の実行によりCommands::AnnotateModelsのインスタンスメソッドのcallが呼び出されます。
@options[:command].call(@options)
注釈実行クラス呼び出し ~ 注釈付与
Commandインターフェースの呼び出し
{Commands::AnnotateModelsインスタンス}.call
上記が呼ばれることで以下の処理が呼ばれます。
# frozen_string_literal: true
module AnnotateRb
module Commands
class AnnotateModels
def call(options)
puts "Annotating models"
if options[:debug]
puts "Running with debug mode, options:"
pp options.to_h
end
# Eager load Models when we're annotating models
AnnotateRb::EagerLoader.call(options)
AnnotateRb::ModelAnnotator::Annotator.send(options[:target_action], options)
end
end
end
end
ここでは、主に以下の処理を行っています。
- 実行に必要なファイルのload
- 注釈付与を行うクラスの呼び出し
加えてここでは、コマンドパターンが採用されています。(多分) commandsという命令専用の空間を作成し、すべてのクラスで同様のcallメソッドを持ちます。
注釈処理の入口
上述で以下が呼び出されています。
AnnotateRb::ModelAnnotator::Annotator.send(options[:target_action], options)
以下が呼び出されます。
# frozen_string_literal: true
module AnnotateRb
module ModelAnnotator
class Annotator
class << self
def do_annotations(options)
new(options).do_annotations
end
def remove_annotations(options)
new(options).remove_annotations
end
end
def initialize(options)
@options = options
end
def do_annotations
ProjectAnnotator.new(@options).annotate
end
def remove_annotations
ProjectAnnotationRemover.new(@options).remove_annotations
end
end
end
end
ここでは、注釈処理の具体的な部分は専用クラスに委譲し、適切なクラスに処理を振り分けることを行なっています。
具体的な注釈処理
上述で呼び出される注釈の具体的な処理が以下です。
# frozen_string_literal: true
module AnnotateRb
module ModelAnnotator
class ProjectAnnotator
def initialize(options)
@options = options
end
def annotate
project_model_files = model_files
annotation_instructions = project_model_files.map do |path, filename|
file = File.join(path, filename)
if AnnotationDecider.new(file, @options).annotate?
_instructions = build_instructions_for_file(file)
end
end.flatten.compact
annotated = annotation_instructions.map do |instruction|
if SingleFileAnnotator.call_with_instructions(instruction)
instruction.file
end
end.compact
if annotated.empty?
puts "Model files unchanged."
else
puts "Annotated (#{annotated.length}): #{annotated.join(", ")}"
end
end
.
.
.
.
end
ここでは主に以下の処理を行っています。
- 注釈を行う必要があるかのチェック
- 注釈付与に必要なカラム情報などを文字列として取得
- 取得した情報を対象のファイルに書き出す
結果的に以下のようにModelファイル等に注釈が付与されます。
# == Schema Information
#
# Table name: users
#
# id :integer not null, primary key
# name :string
# created_at :datetime not null
# updated_at :datetime not null
#
class User < ApplicationRecord
end
図解
図解してみると以下のようになります。
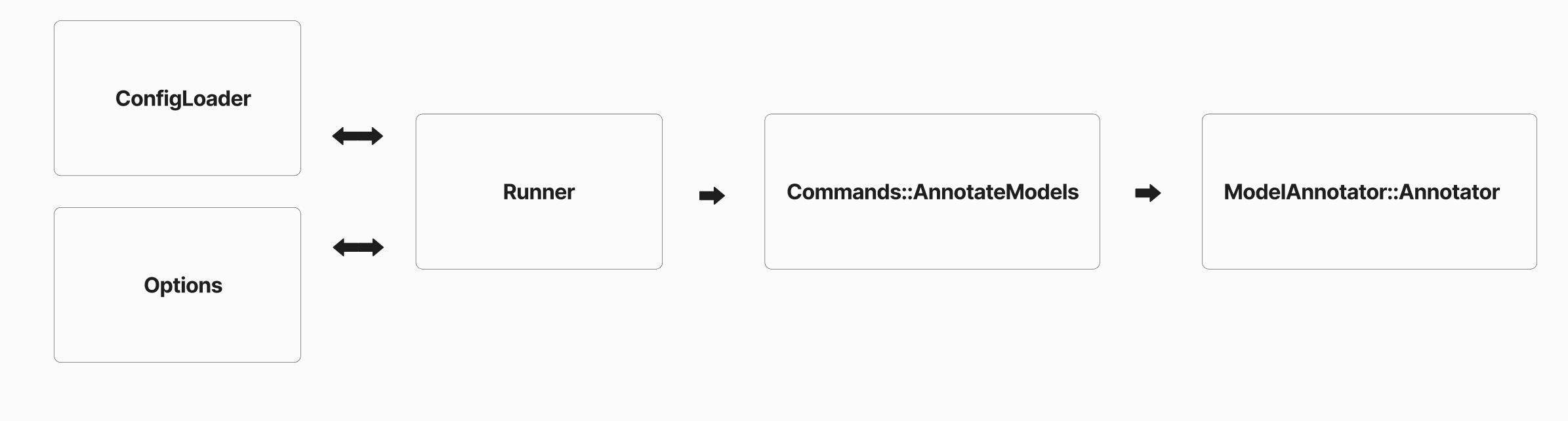
大きく4つの部分に分けることができます
- ConfigLoader: 設定ファイル -> Rubyオブジェクトに変換
- Options: 設定事項、引数をインスタンス変数として格納
- Commands::AnnotateModels: 指定されたコマンドに沿って、注釈実行クラスを呼ぶ
- ModelAnnotator::Annotator: 実際の注釈を担う
所感
コードを読んでいく中で、見たことないメソッドやイディオム、設計方法と出会うことができました。中でもCommandsパターンを見た時には、「なるほどな~」と感動しました。またgemを通して読むのは初めてだったので隅々まで読みましたが、かなり時間がかかりました…;; 時間がかかった原因はおそらく、ある程度の流れを知らない状態で読み進めてしまい、「いまはどこの処理を追っているんだっけ?」となってしまったことだと考えています。なので、次はインタフェースとして提供されているメソッドを追ってある程度構造を把握してから、詳細を読むという方法を試してみようと思います。
なにはともあれ、とても読みやすく書かれているなと思いました。ところどころTODOコメントが残っているので、PRを投げてみようと思います。